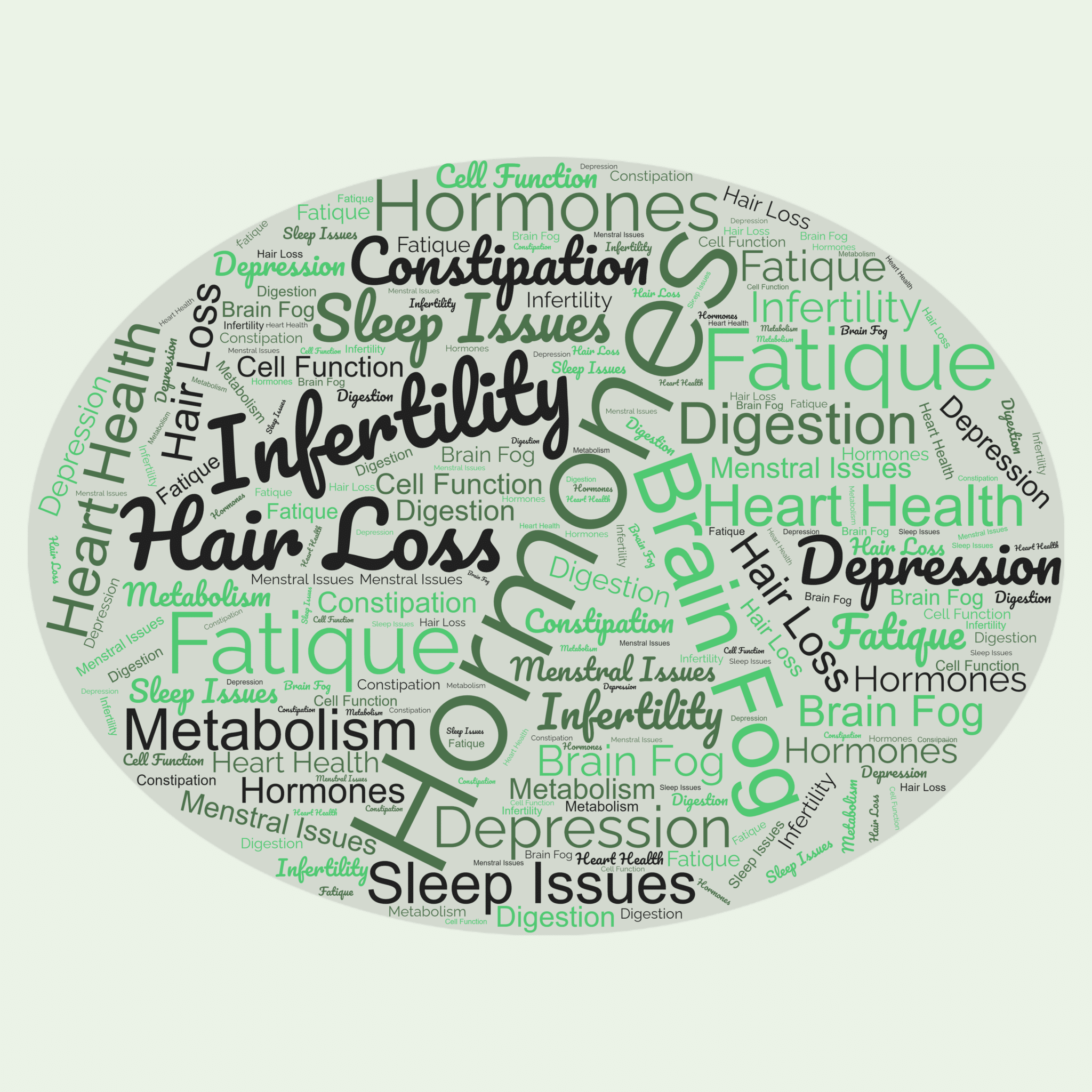index
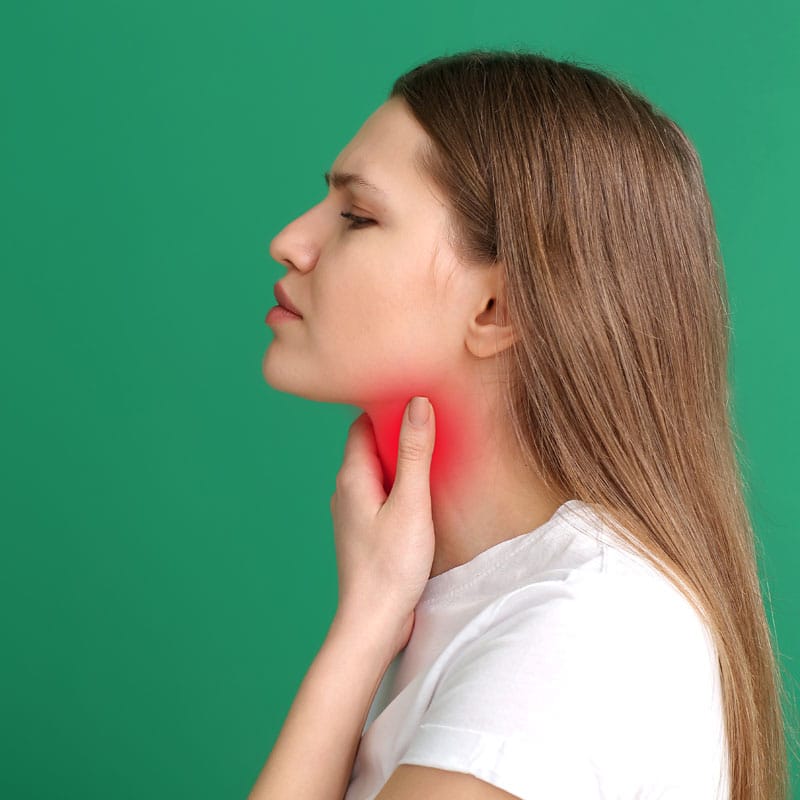
The thyroid gland produces thyroid hormones, which regulate many functions in the body. For example, thyroid hormones control your heart rate, your metabolic rate, brain development, digestive health, muscle development, and bone health. Thyroid gland dysfunction can lead to a myriad of symptoms, both physical and emotional. A person with hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, thyroid cancer, and thyroid related eye disease may experience a rollercoaster of emotional challenges including mood swings, depression, and anxiety. This emotional rollercoaster can be difficult to understand. At one minute, you may be feeling fine, and then the next minute, you are crying or anxious.

Does Thyroid Imbalance Affect Your Mood?
Thyroid imbalances can affect your mental health. In fact, many of the symptoms of thyroid problems can mimic the symptoms of mood disorders. There are many treatment options available for treating thyroid conditions; however, when a thyroid condition begins to affect mood, it becomes even more important to address mental health concerns as well.
Unbalanced thyroid levels can be caused by either hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. Each of these conditions cause different signs and symptoms.
- Hyperthyroidism occurs when your thyroid gland is overactive and produces too much thyroid hormone. Common symptoms include anxiety, mood swings, impatience, a short temper, panic attacks, tenseness, and sleeping difficulties.
- Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland is underactive and does not produce enough thyroid hormone. Common symptoms include decreased appetite, decreased motivation, depression, mood swings, overwhelming stress, concentration issues, sleep disturbances, and a short temper.
Nourish Your Thyroid and Improve Your Mood
The first thing to do if you suffer from a thyroid problem that has affected your mood is to talk with your doctor or nurse practitioner. There are many strategies that can be used to balance your mood as well as certain nutrients and herbs to help your body adapt to changing hormone levels. It will help to consume a diet filled with fresh fruits and veggies, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats.
- Selenium – Selenium deficiency can increase the risk of developing autoimmune thyroid disease. In fact, the thyroid gland contains more selenium than any other organ in the body. Selenium provides anti-inflammatory properties and is neuroprotective. Selenium is used in antioxidant activity in the body to reduce free radical damage. It also helps prevent depression and improve your mood.
- Iodine – The thyroid gland converts tyrosine and iodine into T3 and T4. If you are not consuming enough iodine, your thyroid gland cannot produce these thyroid hormones. That said, taking excess amounts of iodine can overproduce thyroid hormones and lead to hyperthyroidism. Its important to work with your integrative practitioner to determine whether or not iodine supplementation is right for you.
- Omega 3 – Omega 3 fatty acids are healthy fats that fight inflammation. Grass fed butter, cod liver oil, olive oil, and coconut oil nourish the thyroid gland. Furthermore, the medium chain triglycerides are transformed by the body into energy for immediate use.
- Magnesium – Your body needs magnesium for health. Magnesium helps convert the T4 thyroid hormone into the active form of thyroid hormone, T3. Also, merely taking a magnesium supplement helps the thyroid gland make more thyroid hormone. Finally, magnesium can help counteract the effects of thyroid related insomnia and can help you fall and stay asleep.
- Adaptogenic Herbs – Adaptogenic herbs support the thyroid and increase thyroid hormone production. The most common thyroid stimulating adaptogenic herbs include Ashwagandha, Gotu kola, and Siberian ginseng. In addition to these herbs, American ginseng, Chinese ginseng, Licorice, Spikenard, and bonnet bellflower can improve thyroid health. Reishi mushrooms, five flavor berry, and Chinese foxglove also provide thyroid support.

What to Eat and What to Avoid
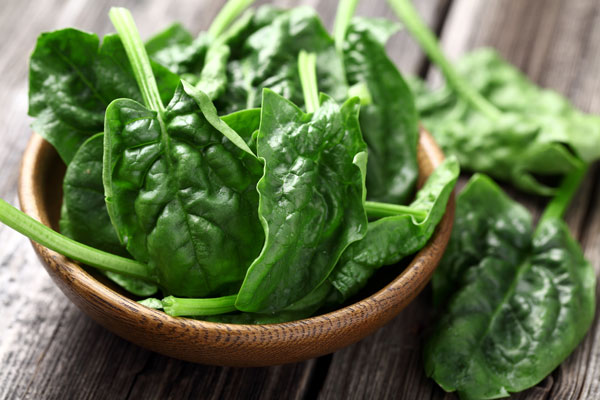
Certain foods provide nutrient support while other foods can block the body’s ability to use iodine. Consuming foods that contain tyrosine such as velvet bean seeds, oats, spinach, sesame seeds, butternut squash, pumpkin seeds, and snow peas help to enhance the thyroid’s ability to produce thyroid hormone and reduce inflammation in the thyroid gland.
Foods that contain goitrogens should be limited. If you decide to include these foods in your diet, cook them as cooking inactivates goitrogens. Goitrogen rich foods include soybeans, cruciferous veggies like cabbage, turnips, broccoli, and kale, peanuts, millet, and pine nuts.
If possible, opt for organic foods whenever possible. Choosing grass-fed meats and wild-caught fish ensures the maximum amount of omega 3 fatty acids are ingested and you get the benefits they offer. Avoid high glycemic index foods, and foods containing gluten as they can increase the risk of inflammation in the thyroid gland.
What Next?
The thyroid gland is a small organ located at the front of the neck. Although small in size, it can greatly impact your health. If the thyroid gland is not functioning properly, you can experience physical problems as well as sudden and severe mood swings. In order to regulate your thyroid hormones and moods, get the assistance of thyroid specialist. Integrative medicine treats the entire person (body, soul, and spirit) rather than just treating the symptoms and an integrative medicine provider will know how to address your thyroid imbalance from a holistic perspective.